Nossos serviços estão apresentando instabilidade no momento. Algumas informações podem não estar disponíveis.
RMPG - Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network - RMPG
Description
Whole set of tide gauge stations, i.e., equipment for monitoring the variations of the sea level, installed and operated by the IBGE, aiming at monitoring the relation between the Brazilian Vertical Datum (established in Imbituba, in Santa Catarina, and in Santana, in Amapá) and other tide gauge reference levels, as well as subsidizing the updating studies of the Brazilian altitudes and variation of the sea level.
About the publication - Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network
Set of tide gauge stations, i.e., equipment, installed and operated by the IBGE, for monitoring the changes in the sea level, aiming at monitoring the relation between the Brazilian Vertical Datum – established in Imbituba, in Santa Catarina, and in Santana, in Amapá – and other tide gauging reference levels, as well as at subsidizing the studies on the modernization of the Brazilian altitudes and on the variations of the sea level.
On the RMPG
One of the actions developed by the IBGE to fulfill its institutional mission is establishing a homogeneous set of geodetic landmarks with high-precision altitudes in the entire Brazilian territory. This set of geodetic landmarks is formally called the High-Precision Altimetric Network - RAAP of the Brazilian Geodetic System - SGB.
Currently, most of the RAAP altitudes are related to the Imbituba Datum, i.e., to the average sea level at the Port of Imbituba (SC) between 1949 and 1957. The small portion of the RAAP existing in Amapá could not be connected to the Imbituba Datum because the mouth of the Amazon River at the Marajó Island could not be crossed by the technique of high-precision geometric leveling, causing the average sea level at the Port of Santana between 1957 and 1958 to be used.
The RMPG was conceived in 1996 by the IBGE´s Department of Geodesy – now the Coordination of Geodesy (CGED) – aiming at establishing and following up the temporal and spatial evolution of the altimetric referential of the SGB. New uses of these data have been developed later, like, for instance, the interface with spatial altimetric missions, which helps to model the topography of the average sea level - TNMM along the Brazilian coastline and to include this information in the mathematical modeling of the Geodetic Boundary Value Problem - PVCG.
Despite the geodetic purpose, the information produced by the RMPG stations are useful for a number of non-geodetic applications, like the reduction of drilling for the conservation and capacity expansion of ports and waterways, implementation of infrastructure – ports, roads, water and sewage networks, etc. – in coastal regions, and study of possible measures to adapt and mitigate the impact of the rise in the average sea level, among other applications.
Characterization
The RMPG stations follow guidelines from the UNESCO´s Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission - IOC, having at least two sensors of observation of the sea level in order to ensure data redundancy and mitigate the lack of information due to any instrumental failure. The types of sensors used are: radar, with a ± 2 mm precision; electronic float and counterweight, with a ± 2 mm precision; and hydrostatic pressure, with a ± 5 mm precision. This last type is used just as a secondary sensor, as it tended to drift in previous analyses in Imbituba, Macaé and Santana, which used to have this type of sensor only. Every station meets the IOC specification of accuracy better than 1 cm under any possible environmental condition (rain, thunderstorm, heavy swell and others).
The system of data transmission is also redundant, counting at least on two independent systems. The types used by the RMPG are dial-up modems, GPRS/GSM modems and GOES antennas. Some stations have also meteorological sensors (atmospheric pressure, temperature and humidity, atmospheric precipitation and wind direction and intensity), which help to refine tide gauging data. In addition, every station is provided with tide scales, vertical wells for the sea level sensors and solar panels to supply energy. The CGED maintains autonomous stations in the RMPG, operating 24 hours a day, during seven days a week.
The RMPG stations contribute to the Global Sea Level Observing System - GLOSS), under the coordination of the Directorate of Hydrography and Navigation - DHN of the Brazilian Navy. Some stations transmit at near real time (5 minutes) to the IOC´s GLOSS Active Network service, directly contributing to the Tsunami Warning subnet in the Caribbean. The link of this service is http://ioc-sealevelmonitoring.org/index.php
Periodically, the RMPG stations are submitted to the Geodetic Control of Tide Gauge Stations - CGEM, with scientific leveling with a 1.5mm √K precision, Van de Casteele Test and GNSS tracking with 3 6-hour sessions in forced centering devices close to the tide gauge stations. In addition, every RMPG station work with a close RBMC station to ensure the stability control together with CGEM, i.e., in order to detect and quantify non-oceanic vertical movements and allow its correction. More details can be obtained in "Technical Instructions" for CGEM.
Lastly, the RMPG maintains a collection of maregrams from stations that used to have analogical sensors of sea level observations, which worked for many years as a backup of the digital sensors and were gradually replaced by the redundancy of the digital sensors.
Operation
The observations are sent at each 5 minutes to the RMPG Control Center, in the Coordination of Geodesy, in Rio de Janeiro (RJ), where they are organized into daily files, corresponding to the sessions started at 12am and ended at 11:55pm or 11:59pm – coordinated universal time –, depending on whether the time resolution of the sensor is 5 min or 1 min.
Once received the data, new files in txt format are created, in which a quality control of the observations is carried out, as well as the time is reformatted according to the Brasília time zone, not considering any daylight saving time, and the observed data are filtered. Then the txt data files are compressed and made available on the download area of the IBGE web portal. Other information on the treatment of the RMPG data can be obtained in the "Analysis of the Variation of the Average Sea Level in the RMPG Stations" report.
At times, some losses of data may occur, due to problems in the data transmission and lack of energy. As far as possible, the data are recovered as soon as the situation is resolved, in the case of transmission problems. However, the data are lost in cases of lack of energy.
Note: It is requested that the RMPG users cite in their works that the data were made available by the IBGE, responsible for the RMPG project, and that they do not pass the data on to third-parties, yet guide other users to either download them through the IBGE web page (RMPG) or request the data directly to the IBGE through the email ibge@ibge.gov.br.
Publications - Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network
Monitoramento da variação do nível médio do mar nas estações da Rede Maregráfica Permanente para Geodésia : 2001-2020 / IBGE, Coordenação de Geodésia
Material type: Book
Year: 2021Análise do nível médio do mar nas estações da Rede Maregráfica Permanente para Geodésia - RMPG : 2001/2015
Material type: Book
Year: 2016Relatório de monitoramento da variação do nível médio do mar nas estações da Rede Maregráfica Permanente para Geodésia - 2001-2012
Material type: Book
Year: 2013
Learn more - Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network
News and Releases
IBGE inaugurates five new stations of the Brazilian Network for Continuous Monitoring; publishes time series of geodetic networks
The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE) inaugurates today (9) five new stations of...
09/12/2024
Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network´s page is more interactive
Aiming at making the access to sea level data and meteorological data more interactive, the Brazilian...
27/11/2024
IBGE starts operating six new stations of the Brazilian Network for Continuous Monitoring and publishes time series of geodetic networks
The IBGE started operating six mew stations of the Brazilian Network for Continuous Monitoring (RBMC)...
15/12/2023
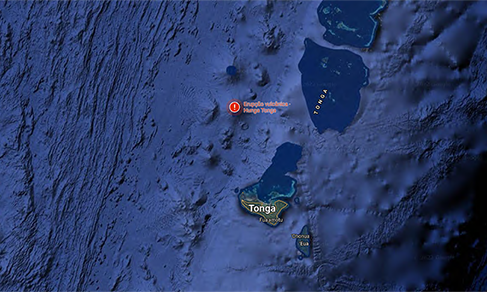
IBGE detects rise in sea level caused by tsunami in Tonga
The tsunami occurred in Tonga Archipelago after a volcanic eruption in the Pacific Ocean on January 15...
21/01/2022
Study brings data from sea level monitoring by IBGE stations
The IBGE makes available today (16) a publication with the results of the monitoring of the variation...
16/12/2021
From large works to prevention of disasters, get to know the functions of geodetic networks
Establishing coordinates for infrastructure works. Demarcating agricultural land. Detecting disturbances...
29/01/2021
Errata
Calendar error in release Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network Portal - RMPG
Published date: 12/08/2024
Description:
Error characterized for not meeting the scheduled release date, according to calendar made available in December 2023. The release was postponed due to the need to readjust the deadlines during the internal steps of their production. The release title was also readjusted from "Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network Portal - RMPG" to "New features on the page of the Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network - RMPG on the IBGE portal."
Therefore, the release "New features on the page of the Geodetic Permanent Tide Gauge Network - RMPG on the IBGE portal" was changed from October to November 2024.Actions: The release calendar has been changed.
Dados diários e situação operacional
Clique nas estações pare ver detalhes sobre cada uma
-

Estações operantes
-

Estações em estado
de advertência -

Estações inoperantes
(sem dados há mais de 6 dias) -

Estações inativas