Nossos serviços estão apresentando instabilidade no momento. Algumas informações podem não estar disponíveis.
Municipalities of the Borderland Strip and Twin Cities
Description
This study reflects Law no. 6,634, of May 2, 1979, regulated by Decree no. 85,064, of August 26, 1980, whose contents were ratified by the 1988 Federal Constitution, in the second paragraph of article 2 - Register of Brazilian municipalities with total or partial area located in the Borderland Strip, which is the inside strip with 150 km of width, parallel to the terrestrial dividing line of the national territory, aggregating the existing information – geographic code and municipality name – with those produced in the identification and/or classification of the municipality within the strip, such as: bordering, partially or completely within the strip, references of the capital to the borderline and inside strip limit.
About the publication - 2022
This publication includes the borderland strip, municipal borders and positions of the capitals of the municipalities that comprise the Borderland Strip.
It is an extremely relevant spatial arrangement as it allows to release statistical and geoscientific information supporting the Municipalities within the Brazilian Borderland Strip. This product supports the studies for the development of new specific public policies about the axes of economic development, security, defense, infrastructure and social issues, land use, environment and regional integration, and sustainable as a consequence of the growth of urban and rural agglomerations in the Borderland Strip, mainly by pinpointing the Brazilian political-administrative units under the rules of national security, especially in terms of public works of civil engineering, acquisition or leasing of land by foreign physical or legal persons, special concessions of land and services, economic exploitation and financial aid from the federal administration, as well as subsidizing bilateral and multilateral agreements to improve relations with neighbor countries in the borderland strip.
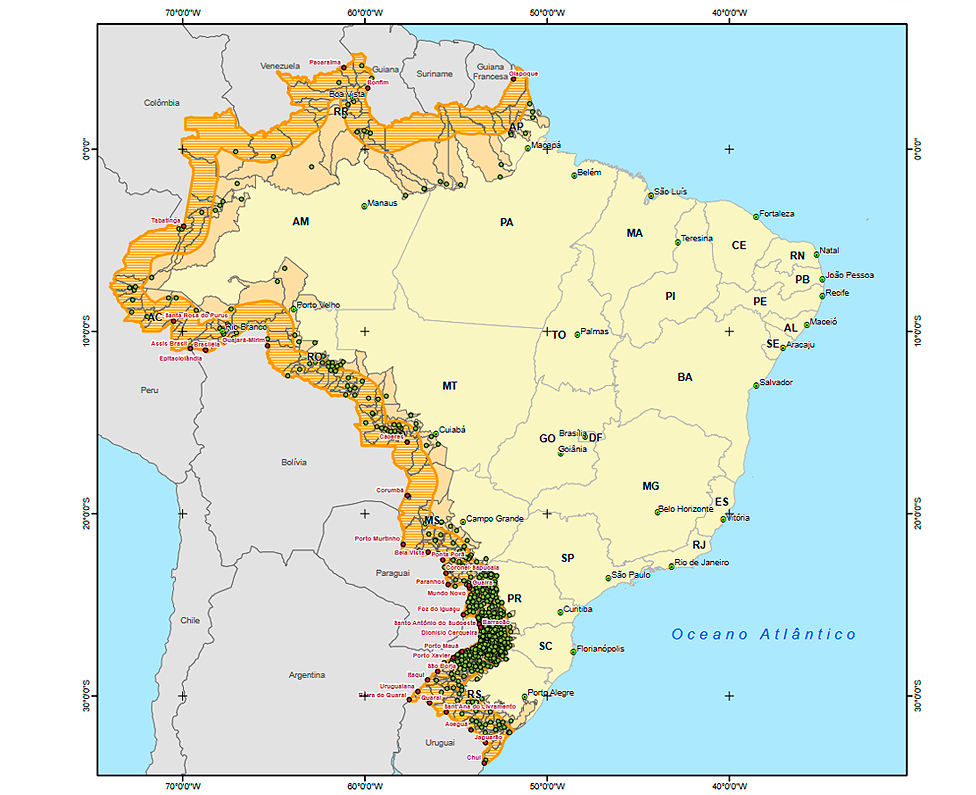
Figure 1 - Municipalities in the Borderland Strip and Twin Cities
Description and Characteristics of the Products
This publication is the result of geoprocessing operations based on the 2022 Digital Municipal Mesh, available on the following address: https://www.ibge.gov.br/en/geosciences/territorial-organization/territorial-meshes/2786-np-municipal-mesh/18890-municipal-mesh.html
Therefore, this publication inherits all the characteristics and conditions of use associated with the 2022 Digital Municipal Mesh.
- The cartographic bases available are compatible with the original scale of work - 1:250,000, without any suppression of points, according to the technical criteria pre-established by IBGE/DGC/CETE.
- Geodetic System of Reference - SIRGAS 2000
- System of Geographic Coordinates
- Text codification - UTF-8
This publication comprises three geospatial files in SHP and KML formats, one spreadsheet in XLS and ODS formats containing only the attributes of the municipalities and one map in PDF format:
Faixa_de_Fronteira_2022: This is the representation of the borders of the Borderland Strip, comprising one polygon. It shows the following attributes:
- NOME: “Faixa de Fronteira”
- AREA_KM2: informs the area in square kilometers.
Faixa_de_Fronteira_por_UF_2022: This is the representation of the borders of the Borderland Strip, comprising 11 polygons representing the area of each FU that has areas within the borderland strip. It shows the following attributes:
- CD_UF: Numeric code associated by the IBGE to the State.
- NM_UF: Name of the State
- SIGLA_UF: Acronym of the State.
- NM_REGIAO: Informs the name of the geographic Region that the State belongs to.
- AREA_KM2: informs the total area of the State in square kilometers.
- CD_MUN: Numeric code associated by the IBGE to the Municipality.
- NM_REGIAO: Informs the name of the geographic Region that the municipality belongs to.
- AREA_INT: Area of the State within the Borderland Strip, expressed in square kilometers.
- PORC_INT: Percentage of the area of the State within the area of the Borderland Strip, expressed in percentage (0 - 100%)
Municipios_Faixa_Fronteira_2022: This is the representation of the polygons of the municipalities that comprise the Borderland Strip. It comprises 590 polygons (588 municipalities plus Lagoa dos Patos and Lagoa Mirim), where 432 municipalities are 100% included in the Borderland Strip. It shows the following attributes:
- CD_MUN: Numeric code associated by the IBGE to the Municipality.
- NM_REGIAO: Informs the name of the geographic Region that the municipality belongs to.
- CD_UF: Numeric code associated by the IBGE to the State that the municipality belongs to.
- NM_UF: Name of the State that the municipality belongs to.
- SIGLA_UF: Acronym of the State that the municipality belongs to.
- NM_MUN: Name of the Municipality.
- AREA_TOT: Total area of the municipality expressed in square kilometers.
- AREA_INT: Area of the municipality within the Borderland Strip, expressed in square kilometers.
- PORC_INT: Percentage of the area of the municipality within the area of the Borderland Strip, expressed in percentage (0 - 100%)
- CID_GEMEA: Informs whether the capital of the municipality has a twin city in any neighbor country. Informs the Legal Act that defined this condition. It is null for capitals that do not have any twin city.
Sede_Municipios_Faixa_de_Fronteira_Cidades_Gemeas_2022: This is the representation of the points that represent the municipal capitals of each municipality of the region. It comprises 588 points. It shows the following attributes:
- NM_REGIAO: Informs the name of the geographic Region that the municipality belongs to.
- CD_UF: Numeric code associated by the IBGE to the State that the municipality belongs to.
- NM_UF: Name of the State that the municipality belongs to.
- SIGLA_UF: Acronym of the State that the municipality belongs to.
- CD_MUN: Numeric code associated by the IBGE to the Municipality.
- NM_MUN: Name of the Municipality.
- LAT_SEDE: Latitude coordinate expressed in decimal degrees.
- LNG_SEDE: Longitude coordinate expressed in decimal degrees.
- CID_GEMEA: Informs whether the capital of the municipality has a twin city in any neighbor country. Informs the Legal Act that defined this condition. It is null for capitals that do not have any twin city.
- SEDE_FAIXA: Informs whether the municipal capital is located inside (“sim”) or outside (“não”) the Borderland Strip.
More on the product - 2022
Municipalities in the Borderland Strip and Twin Cities - XLSX
Municipalities in the Borderland Strip and Twin Cities - ODS
Municipalities in the Borderland Strip and Twin Cities - shapefiles
Capitals of Municipalities in the Borderland Strip and Twin Cities - shapefiles
Municipalities in the Borderland Strip - KML
Capitals of Municipalities in the Borderland Strip and Twin Cities - KML
Municipalities in the Borderland Strip - Map in PDF format
The following files can be found on these links:
|
Mun_Faixa_de_Fronteira_Cidades_Gemeas_2022.xlsx and ODS version |
Spreadsheets |
|
Faixa_de_Fronteira_por_UF_2022_shp.zip |
1 area record |
|
Municipios_Faixa_Fronteira_2022_shp.zip |
588 area records |
|
Sedes_Municipios_Faixa_de_Fronteira_Cidades_Gemeas_2022_shp.zip |
588 point records - excluding Lagoa dos Patos and Lagoa Mirim |
|
Municipios_Faixa_Fronteira_2022.kml |
590 area records |
|
Sedes_Municipios_Faixa_de_Fronteira_Cidades_Gemeas_2022.kml |
588 point records - excluding Lagoa dos Patos and Lagoa Mirim |
|
Municipios_da_Faixa_de_Fronteira_2022.pdf |
Map in PDF |
Learn more - 2022
News and Releases
IBGE updates geographic divisions of reference to disseminate results of 2022 Census
The IBGE released today (19) the 2022 edition of the Geographic Reference Framework for the Production,...
19/07/2023
IBGE releases updating of legal territorial divisions of Brazil
The IBGE releases today (14) an updating of the legal territorial divisions of Brazil. Altogether, they...
14/07/2022
IBGE updates municipalities in borderland strip and facing the sea due to changes in limits
The IBGE releases today (06) two products that update the list of municipalities of the borderland strip...
06/07/2021
IBGE releases list of municipalities in borderland strip (2)
The IBGE released today (22) the list of the 588 municipalities located in the borderland strip of Brazil,...
22/06/2020
Geospatial technologies improve border of Brazil with South America
To accomplish these changes with ten neighbor countries, the IBGE queries the Ministry of Foreign Relations´...
22/06/2020
IBGE releases list of municipalities in borderland strip
The IBGE releases today the list of the 588 municipalities located in the Brazilian borderland strip,...
27/03/2019









