Nossos serviços estão apresentando instabilidade no momento. Algumas informações podem não estar disponíveis.
Mesh of Enumeration Areas
Description
It is a compilation, in digital format, of the smallest territorial portion used by IBGE to plan and carry out data collection for the Census and Statistical Surveys: the Enumeration Area. This corresponds to a section of the national territory, considering the Political-Administrative Division and other territorial structures, which allows the collection of statistical information within the due collection period.
It depicts the stage of IBGE's cadastral systems in time, according to the processes of data acquisition, treatment, management and updating, to be used in the construction of the Census Mapping for the Population Censuses and Household Surveys. It constitutes an overview of the Brazilian Political-Administrative Division in force on the reference date, including States, Federal District, Municipalities, Districts and Subdistricts, whose cadastral identification comprises the code of the enumeration area. In addition, each enumeration area brings information capable of organizing the collection, such as its urban or rural location/feature and status of locations, such as cities, villages, urban centers and rural agglomerations.
As of 2020, it became possible to distinguish the Mesh of Enumeration Area or, simply Census Mesh, from the new product, the Intermediate Mesh of Enumeration Area. The former is linked to the disclosure of the results of operations such as Population Censuses, Censuses of Agriculture and Population Count. In this case, as it is the result of a thorough survey of the Brazilian territory, it will have a much larger set of information than the Intermediate Mesh of Enumeration Areas. This, in turn, will bring annually updated information on territorial changes that affect the form and classification of enumeration areas on a annual basis, although it does not bring the statistical information brought by the former.
About the publication - 2007 Census Mesh
It is a set of files containing the polygons that define municipalities, districts, subdistricts, neighborhoods and enumeration used for the 2007 Census of Agriculture and the Population Counting.
Enumeration Area
The enumeration area control units made up of continuous polygons, entirely contained in urban or rural areas, whose size, number of households and establishments allow the enumerator to carry out his activities within a specified period, respecting the schedule of activities. The enumeration area is the work field of the enumerator.
Each enumaeration areas has an identifying number, called a geocode. It is formed by recomposing the political-administrative hierarchy to which the enumeration area belongs: the first two digits refer to the state code; the subsequent five are related to the municipality; the next two indicate the district; the next two point to the subdistrict; and, finally, the last five to the enumeration area.
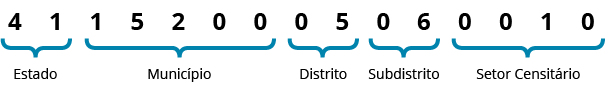
Criteria for delimiting enumeration areas
Enumeration areas are defined to guarantee the collection of census surveys and the dissemination of data by territorial sections. Thus, there are three basic rules for delimiting census sectors:
- minimum and maximum number of households or agricultural establishments: between 150 and 400 in urban areas and, for rural areas, between 150 and 250. As for agricultural establishments, the threshold is 100 to 200 for urban and rural areas.
- its limits should preferably be guided by recognizable elements in the landscape, facilitating the location of the enumerator in the field and allowing him/her to identify the households belonging to his work area;
- its limits must respect the political-administrative division and other territorial areas of data dissemination
The classification of enumeration areas as urban or rural corroborates to the estimate of the urban and rural population.
Classification of the enumeration area by status and type
Enumeration areas are classified by status and types. The status indicates the dispersion or agglomeration of households in the territory, deepening the distinction between urban and rural areas. The types refer to specificities of certain sectors in terms of logistics.
The status are:
- Urbanized City or Town Area (code 1): it is the area legally defined as urban and characterized by high housing density, subdivisions, constructions, streets, intense human occupation and transformations resulting from urban development.
- Non-Urbanized City or Village Area (code 2): it the one legally defined as urban, but characterized by predominantly rural occupation, with a large areas of land and low housing and construction density.
- Isolated Urban Area (code 3): it is the area defined and classified by municipal law, and separated from the municipal (city) or district (village) headquarters by rural area or other legal limit.
- Rural Agglomerate of Urban Extension (code 4): are located in areas outside the legal urban perimeter, formed by the expansion of a city or town, and located less than 1 km from its urban perimeter. or from a rural settlement already defined as an urban extension.
- Settlement (code 5): is the isolated rural settlement without a private or business nature, that is, not linked to a single landowner (agricultural company, industries, plants, etc.), whose residents carry out primary economic activities (wild-crop harvesting, animal farming, mining and livestock activities), or secondary (industry in general) or tertiary (trade and services) in the agglomerate itself or outside it. To be isolated in a sector, the agglomerate must contain at least 50 households, not more than 50m apart from one another.
- Nucleus (code 6): is the isolated rural agglomerate linked to a single landowner (agricultural company, industry, plant, agricultural and rural tourism establishments, etc.) with or without the defining village services or equipment. It is thus considered, as it has a private or business nature, as a defining characteristic. To be isolated in a sector, they must contain at least 50 households, not more than 50m apart from one another.
- Village (code 7): isolated rural agglomerate that does not have, fully or partially, the defining urban services or equipment that define settlements and that are also not linked to a single owner (agricultural company, industry, plant, etc.). To be isolated in a sector, they must contain at least 50 households, not more than 50m apart from one another.
- Rural Area (code 8): it is one that was not included in the urban perimeter by municipal law. It is characterized by rustic land use, with large tracts of land and low housing density. They include fields, forests, crops, pastures, etc.
The types are:
- Non-Special (code 0): enumeration areas in which standard procedures for collecting interviews from the Census of Agriculture and Population Counting were adopted.
- Enumeration Areas in Subnormal Agglomerates (code 1): it is a set of housing units, located in urban areas, of illegal land occupation, in the current or recent period, and which presents at least one of the following characteristics: asymmetrical urban pattern of roads/circulation and of size and shape of the lots, lack of essential public services, such as sewage, water, electricity and public lighting.
- Enumeration Areas in Barracks and Military Bases (code 2): military barracks and bases with at least 50 residents.
- Enumeration Areas in Lodging and Camping (code 3): accommodations and campings with at least 50 residents.
- Enumeration Areas in Vessesl and Ships (code 4): vessels and ships with at least 50 residents.
- Enumeration Areas in Indigenous Villages (code 5): it is the house or the set of houses or malocas, which can also be understood as an address, which serves as lodging and accommodation of several indigenous families gathered together.
- Enumeration Areas in Penitentiary, Penal Colony, Prisons or Jails (code 6): prison units with at least 50 residents.
-
Enumeration Areas in Asylums, Orphanages, Convents or Hospital Sectors (code 7): asylums, orphanages, convents or hospitals with at least 50 residents.
Enumeration Areas in Agrovilas of Settlement Projects (PA) (code 8): agrovilas are basic forms of rural organization, where families who live close to each other share a an area for leisure, services and social interaction. Agrovilas of PAs are those that are formed from settlement projects.
More on the product - 2007 Census Mesh
Learn more - 2007 Census Mesh
Setor Censitário
O setor censitário é a unidade de controle cadastral formada por área contínua, integralmente contida em área urbana ou rural, cuja dimensão, número de domicílios e de estabelecimentos permitem ao recenseador cumprir suas atividades em um prazo determinado, respeitando o cronograma de atividades. O setor censitário é a área de trabalho do recenseador.
Cada setor censitário possui um número identificador, denominado geocódigo. É formado através da recomposição da hierarquia político-administrativa a qual o setor censitário pertence: os dois primeiros dígitos se referem ao código do estado; os cinco subsequentes se relacionam ao município; os dois seguintes indicam o distrito; os dois na sequência apontam o subdistrito; e, por fim, os cinco últimos ao setor censitário.
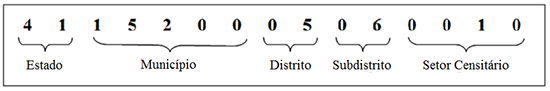
Critérios para delimitação dos setores censitários
Os setores censitários são definidos para garantir a coleta das pesquisas censitárias e a divulgação de dados por recortes territoriais. Assim, existem três regras básicas de delimitação dos setores censitários:
- número mínimo e máximo de domicílios ou estabelecimentos agropecuários: entre 150 e 400 nas áreas urbanas e, para as áreas rurais, entre 150 e 250. Quanto aos estabelecimentos agropecuários, o limiar é de 100 a 200 para áreas urbanas e rurais. Os setores de aglomerados rurais devem ter no mínimo 50 domicílios para serem isolados em setores censitários e para as aldeias indígenas o critério é 20 indígenas;
- limites do setor censitário devem, preferencialmente, ser pautados por elementos reconhecíveis na paisagem, facilitando a localização do recenseador em campo e permitindo que este identifique os domicílios pertencentes a sua área de trabalho;
- limites do setor censitário devem respeitar a divisão político-administrativa e demais recortes territoriais de divulgação dos dados
Classificação do setor censitário por situação e tipo
Os setores censitários recebem a classificação por situações e tipos. As situações indicam a dispersão e aglomeração de domicílios no território, servindo a um detalhamento da distinção de áreas urbanas e rurais. Os tipos se referem a especificidades de determinados setores quanto a coleta de entrevistas nos Censos.
As situações são:
- Área Urbanizada de Cidade ou Vila (código 1): é a área legalmente definida como urbana e caracterizada por alta densidade habitacional, loteamentos, construções, arruamentos, intensa ocupação humana e transformações decorrentes do desenvolvimento urbano.
- Área não Urbanizada de Cidade ou Vila (código 2): é aquela legalmente definida como urbana, porém caracterizada por ocupação predominantemente rural, apresentando grande extensão de terra com baixa densidade habitacional e construtiva.
- Área Urbana Isolada (código 3): é a área definida e denominada por lei municipal, e separada da sede municipal (cidade) ou distrital (vila) por área rural ou por outro limite legal.
- Aglomerado Rural de Extensão Urbana (código 4): aglomerados rurais de extensão urbana são localidades situadas em áreas fora do perímetro urbano legal, desenvolvidos a partir da expansão de uma cidade ou vila, e localizadas a menos de 1 km de distância do seu perímetro urbano ou de um aglomerado rural já definido como de extensão urbana.
- Povoado (código 5): é o aglomerado rural isolado sem caráter privado ou empresarial, ou seja, não vinculado a um único proprietário do solo (empresa agrícola, indústrias, usinas etc.), cujos moradores exercem atividades econômicas primárias (extrativismo vegetal, animal e mineral, e atividades agropecuárias), secundárias (industriais em geral) ou terciárias (comércio e serviços) no próprio aglomerado ou fora dele. Para serem isolados em setor devem conter no mínimo 50 domicílios, distantes entre si não mais que 50m.
- Núcleo (código 6): é o aglomerado rural isolado vinculado a um único proprietário do solo (empresa agrícola, indústria, usina estabelecimentos agropecuários e de turismo rural etc.) dispondo ou não dos serviços ou equipamentos definidores dos povoados. É assim considerado, pois possui caráter privado ou empresarial, como característica definidora. Para serem isolados em setor devem conter no mínimo 50 domicílios, distantes entre si não mais que 50m
- Lugarejo (código 7): aglomerado rural isolado que não dispõe, no todo ou em parte, dos serviços ou equipamentos urbanos definidores dos povoados e que também não estão vinculados a um único proprietário (empresa agrícola, indústria, usina etc.). Para serem isolados em setor devem conter no mínimo 50 domicílios, distantes entre si não mais que 50m
- Área Rural (código 8): é aquela que não foi incluída no perímetro urbano por lei municipal. Caracteriza-se pelo uso rústico do solo, com grandes extensões de terra e baixa densidade habitacional. Incluem campos, florestas, lavouras, pastos etc.
Os tipos são:
- Não-Especial (código 0): setores censitários em que adotou-se os procedimentos padrões na coleta de entrevistas do Censo Agropecuário e da Contagem da População.
- Setor Censitário de Aglomerado Subnormal (código 1): é um conjunto de unidades habitacionais, localizadas em áreas urbanas, de ocupação ilegal da terra, no período atual ou recente, e que apresenta pelo menos uma das seguintes características: padrão urbanístico assimétrico das vias de circulação e do tamanho e forma dos lotes, carência de serviços públicos essenciais, como rede de esgoto, rede de água, energia elétrica e iluminação pública.
- Setor Censitário de Quartel e Base Militar (código 2): quartéis e bases militares com no mínimo 50 moradores.
- Setor Censitário Alojamento e Acampamento (código 3): alojamentos e acampamentos com no mínimo 50 moradores.
- Setor Censitário de Embarcações e Navios (código 4): embarcações e navios com no mínimo 50 moradores.
- Setor Censitário de Aldeia Indígena (código 5): é a casa ou o conjunto de casas ou malocas, podendo ainda ser entendida como morada, que serve de habitação e aloja diversas famílias indígenas reunidas.
- Setor Censitário de Penitenciária, Colônia Penal, Presídio ou Cadeia (código 6): unidades prisionais com no mínimo 50 moradores.
- Setor Censitário de Asilo, Orfanato, Convento ou Hospital (código 7): asilo, orfanato, convento ou hospital com no mínimo 50 moradores.
- Setor Censitário de Agrovila do Projeto de Assentamento (PA) (código 8): as agrovilas são formas básicas de organização rural, onde famílias que residem próximas umas das outras compartilham um espaço comunitário de lazer, serviços e convívio social. As Agrovilas dos PAs são aquelas que se desenvolvem a partir dos projetos de assentamento.
News and Releases
IBGE launches Intermediate Sectoral Mesh 2021
The IBGE releases today (21) the Intermediate Sectoral Mesh 2021 in digital format, including the classification...
21/11/2022
IBGE discloses the 2020 Intermediate Mesh of Enumeration Areas
Today (25) the IBGE publishes the 2020 Intermediate Mesh of Enumeration Areas in digital format, with...
25/02/2021
IBGE launches Intermediate Sectoral Mesh 2019
The IBGE releases today (30) the Intermediate Sectoral Mesh 2019 in digital format, including the classification...
30/07/2020
Errata
Amendment in the release of the 2020 Intermediate Mesh of Enumeration Areas
Published date: 15/03/2021
Description:
Amendment in the release of the 2020 Intermediate Mesh of Enumeration Areas, published on February 25, after determining inconsistencies in the counting of enumeration areas, which were amended from 448,988 to 449,880.
Files in shape and kml format of the "2020 Intermediate Sectoral Mesh" were replaced to correct the field “Sub-district” in the Federal District and the field “District” in the Muncipalities of 2205706 - Luís Correia-PI; 2401305 - Campo Grande-RN; 2601607 - Belém do São Francisco-PE; 3122900 - Dona Euzébia-MG; 4216057 - São Cristóvão do Sul-SC; 4323770 – Westfália-RS; 5000203 - Água Clara-MS; 5001904 – Bataguassu-MS and 5220157 - São Luiz do Norte-GO.Actions: The news was updated at https://agenciadenoticias.ibge.gov.br/en/agencia-press-room/2185-news-agency/releases-en/30121-ibge-divulga-malha-setorial-intermediaria-2021.
The files were replaced at https://www.ibge.gov.br/en/geosciences/territorial-organization/territorial-organization/28114-malhas-de-setores-censitarios-divisoes-intramunicipais-2.html?=&t=o-que-e.
Links






